Despite years of neglect — these are exciting times for the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis (TB)! A new treatment regimen for drug resistant tuberculosis with the potential of cutting treatment time by 75% is gaining traction and a new urine based test may make diagnosis a lot easier. Despite these, challenges remain in Nigeria, especially around the potential for creating a sense of urgency in the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis.
The 2019 National TB Conference will bring together stakeholders and partners to share knowledge, new science and policies. This will drive the tuberculosis community to mobilise needed resources within the public and the private sectors, to increase awareness about TB and inspire action. The conference will bring together key TB stakeholders from Nigeria and across the globe to deliberate on issues relating to TB control and foster collaboration on how to end TB in Nigeria. The conference will take place from July 17–18, 2019 at the International Conference Centre in Abuja.
According to the World Health Oranization (WHO), Nigeria is among the 10 countries that account for 64% of the global gap in TB case findings. India, Indonesia and Nigeria account for almost half of the total gap. Nigeria is one of the 14 countries listed in all three of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) global lists of high burden countries for TB, TB/HIV and multi-drug resistant (MDR)-TB. Numerous strategies have been utilised by past and present Nigerian governments to reduce and eliminate the spread of Tuberculosis (TB) in the country. Yet, progress in the detection of new cases has remained low. It is estimated that in Nigeria, 407,000 HIV negative and 63,000 HIV positive people are infected with TB every year. In 2017 only, 104,904 TB cases were detected out of the estimated 407,000 of all TB cases expected to be detected that year, based on prevalence estimates in Nigeria. Nigeria struggles with low TB case finding for both women and children. The increasing gap in access to TB services for children and other vulnerable groups is also of great concern. This means that only 25% of TB patients are on treatment, while 75% remain untreated, worsening the disease burden.
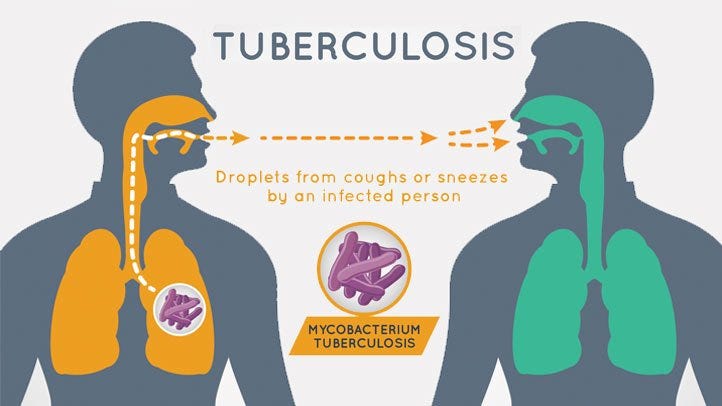
Nigeria does have a plan to control TB — the National Strategic Plan (NSP) for tuberculosis control was developed to ensure universal access to high-quality, patient-centered prevention, diagnosis and treatment services for TB, TB/HIV and drug-resistant TB by 2020. However, funding constraints have remained the key challenge towards its implementation. Long-term government commitment is critical for implementing the intensive efforts needed to bring TB under control in Nigeria.
To achieve the ambitious plan and address TB challenges by 2020, Nigeria needs about $336m (N11.8bn). With a current budget of just $121m, Nigeria’s estimated gap in funding the strategic plan is put at about $215m, about 64%. TB funding over the years has been driven by external funding sources. The Stop TB Partnership Nigeria was established in 2007 to advocate for more resources, including human resources, technical expertise, financial resources and in-kind contributions, from partners in the country and from international donors towards supporting the TB control response in Nigeria. The TB control efforts in Nigeria are in line with the Global Strategy and Targets for tuberculosis prevention, care and control 2015 to 2035.
The plan has some ambitious targets —
1. To reduce TB deaths by 95%
2. To cut new cases by 90%
3. To ensure that no family is burdened with catastrophic expenses due to TB by 2035.
This year’s conference will focus on developing partnerships and innovations for Tuberculosis Care and Treatment. The event will provide a platform to foster the designing of evidence-based policies for improved TB control in Nigeria.
Themed, “Building stronger partnerships to end TB in Nigeria” the National TB Conference 2019 will include sub-themes around the key arrears in TB control, including;
• Stakeholders engagement in TB control
• Childhood Tuberculosis
• TB/HIV co-infection
• Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
• Tuberculosis in prisons and IDP
• Tuberculosis prevention (TPT) and infection control
• Innovations in TB case finding diagnosis and treatment.
• Public-Private Mix in TB control.
It will provide ample opportunities for stakeholders and policymakers involved in TB control and academia to access research, technologies and innovations in TB control in Nigeria. The ultimate goal is to stimulate the generation of new collaborations for homegrown TB research and innovation, as the drive to #EndTBInNigeria gains momentum.
Watch this video on why tuberculosis is the world’s most infectious killer?
The conference is open to the general public. Participants should register online.